Symmetry, Biology, Types, Examples, & Facts

By A Mystery Man Writer
Symmetry, in biology, the repetition of the parts in an animal or plant in an orderly fashion. Specifically, symmetry refers to a correspondence of body parts, in size, shape, and relative position, on opposite sides of a dividing line or distributed around a central point or axis.

Phylum Porifera - Characteristics and Examples

27.2A: Animal Characterization Based on Body Symmetry - Biology LibreTexts

Organismal Biology

The principle of symmetry in graphic design
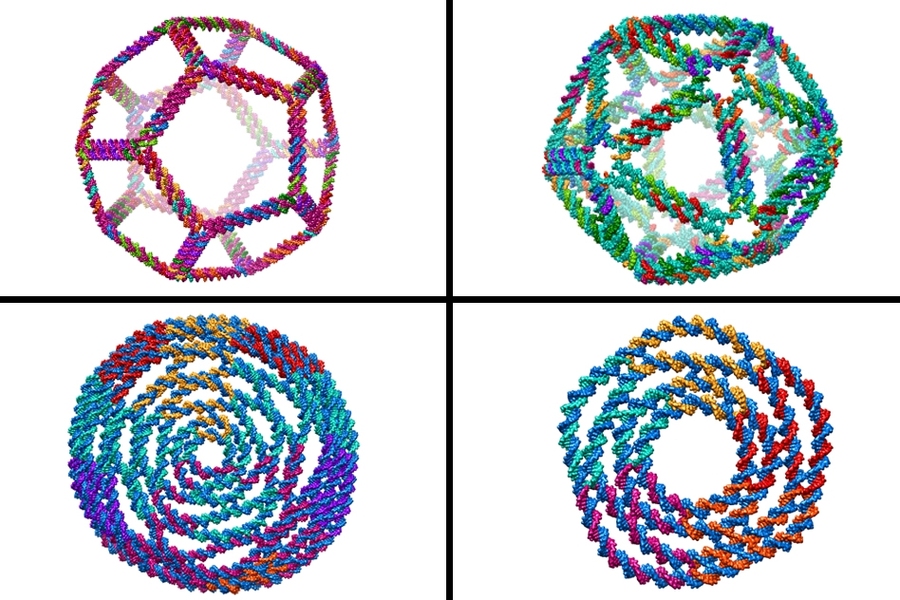
Computer model enables design of complex DNA shapes, MIT News

Symmetries of a Graph - Maple Help

Bilateral Symmetry - Definition and Examples

Symmetry in biology - Wikipedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/skewness-Final-e6e1970b817443f897a4a65d2c5b92d1.jpg)
Right Skewed vs. Left Skewed Distribution
Sorting Symmetrical Shapes Worksheets

5 Groups of Vertebrates - Characteristics and Examples
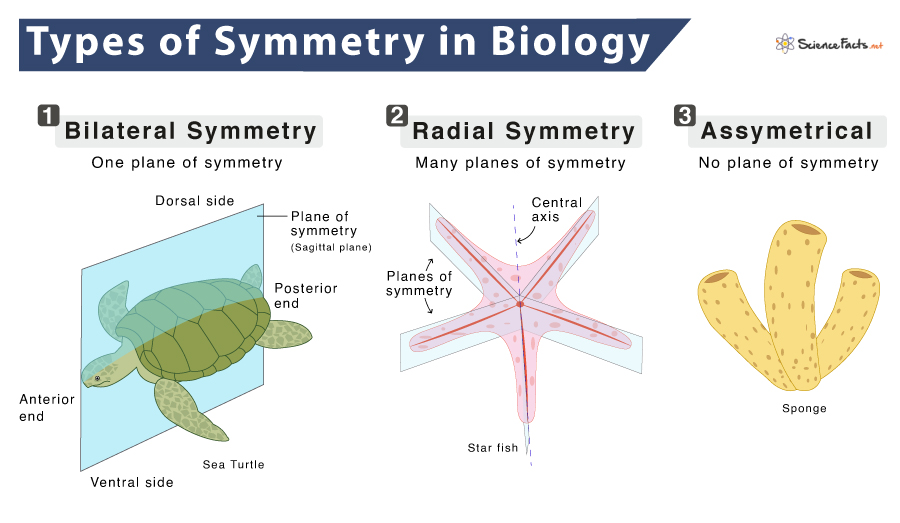
Symmetry in Biology – Radial vs. Bilateral Symmetry

Symmetry, Biology, Types, Examples, & Facts

Cell Differentiation, Tissue
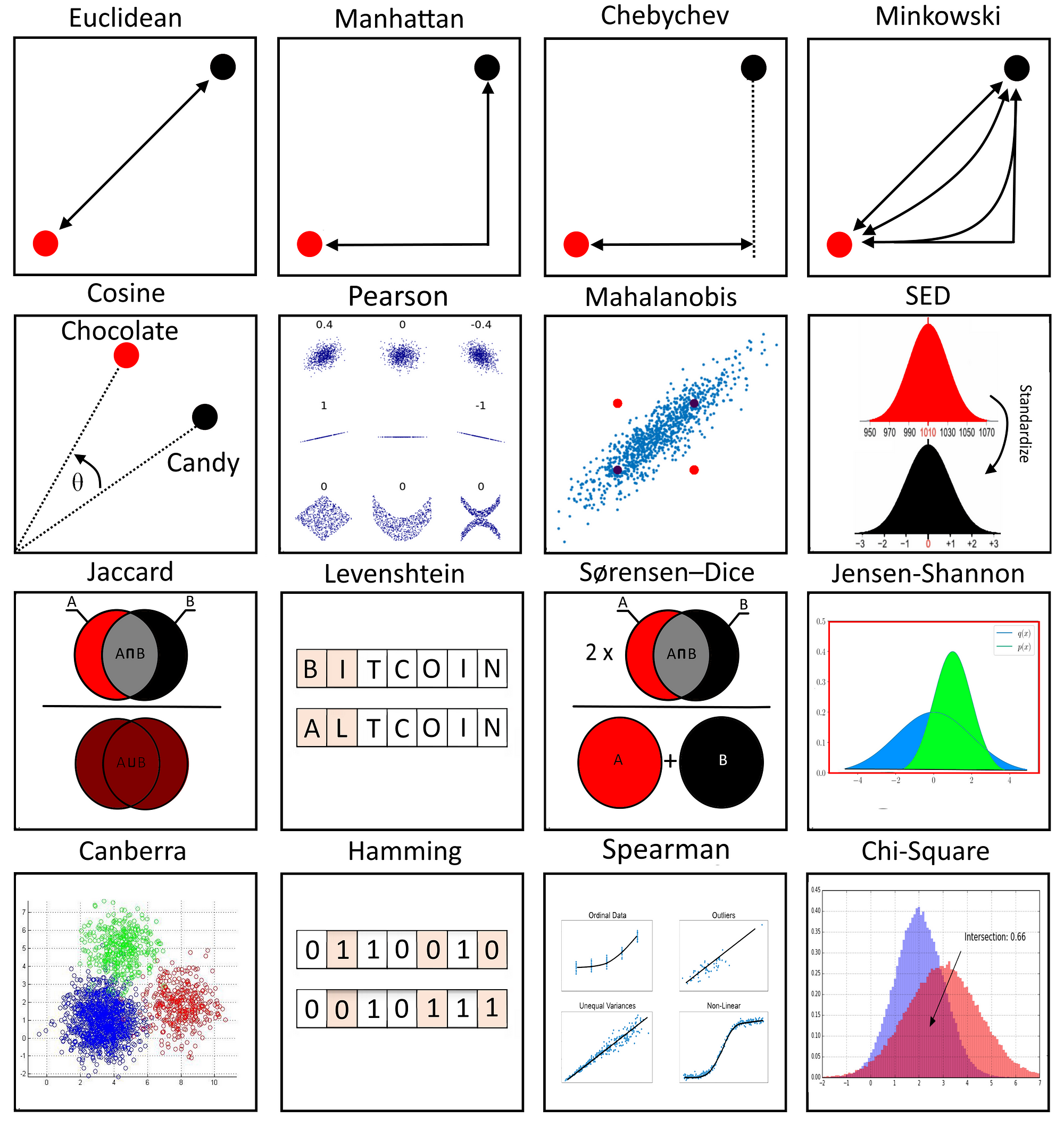
17 types of similarity and dissimilarity measures used in data science., by Mahmoud Harmouch