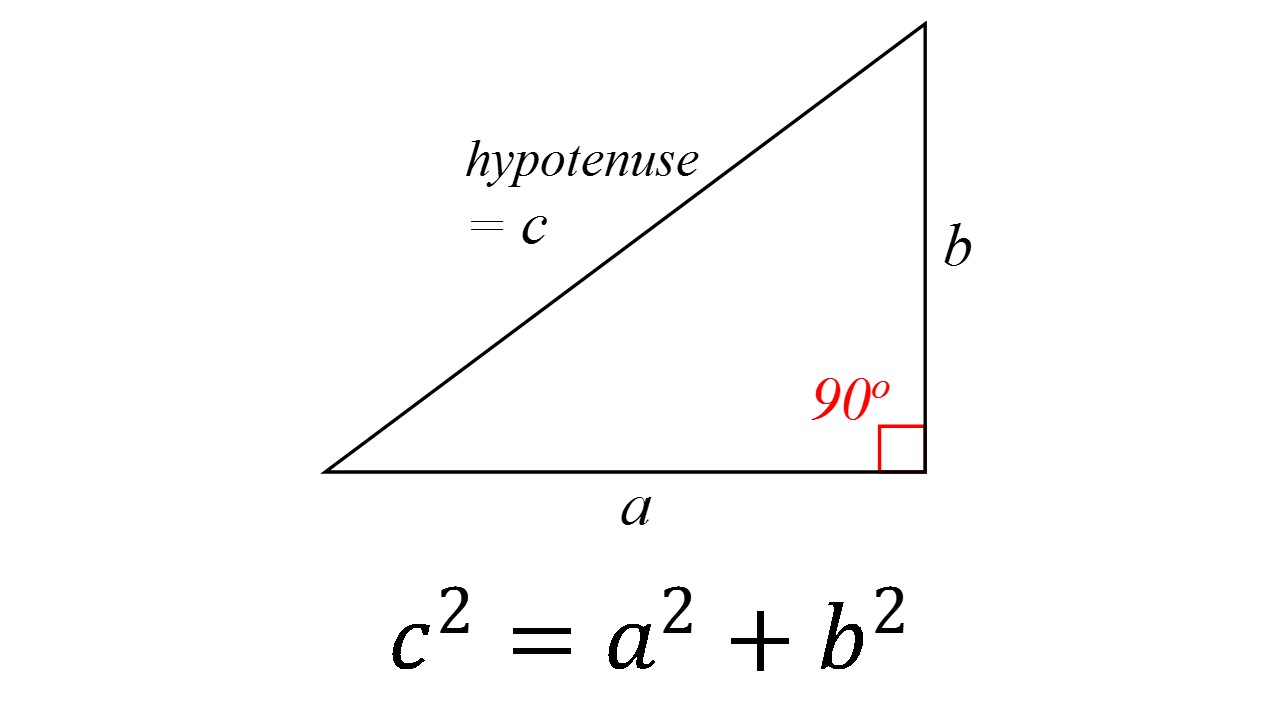
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?
By A Mystery Man Writer
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.

Pythagorean Triple, Definition, List & Examples - Lesson
What are the measures of the acute angles in a right triangle with
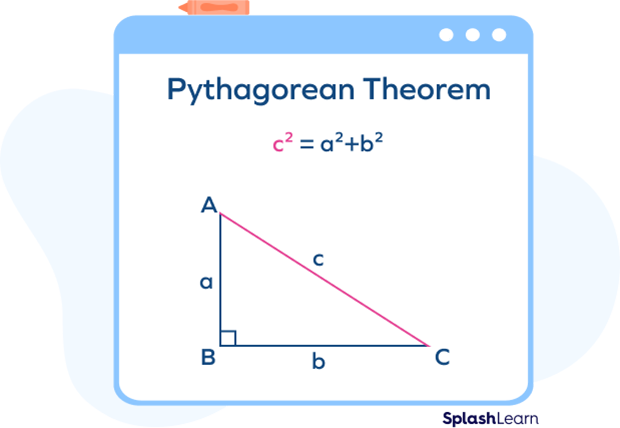
Pythagorean Triples - Definition, Formula, Examples, Facts

Pythagorean Triples - Definition, Formula, Examples
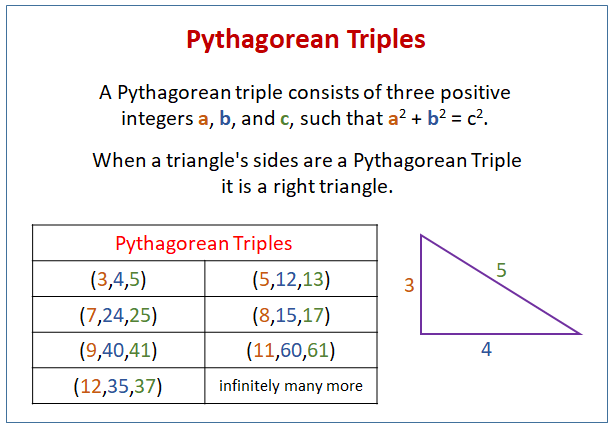
Pythagorean Triples (video lessons, examples, step-by-step solutions)

How To Verify A Triangle Is A Right Triangle Using The Pythagorean
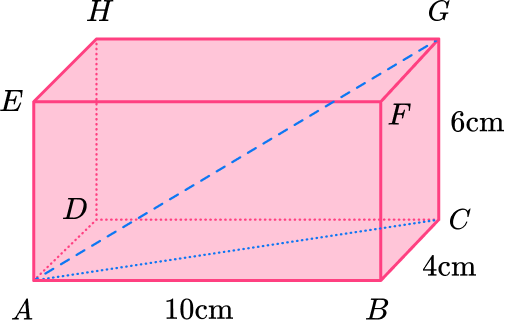
Pythagorean Theorem - Math Steps, Examples & Questions

Pythagoras Theorem Questions (with Answers) – Math Novice

The Converse of Pythagorean Theorem

Pythagorean Theorem Calculator - Quadratic Formula Calculator

Pythagorean theorem - Wikipedia

Right Triangles

Right Angled Triangle - Formula, Properties
- Isosceles Right Triangle - Formula, Properties, Area, Examples

- Basic Right Triangle Trigonometry - Carolina Knowledge Center
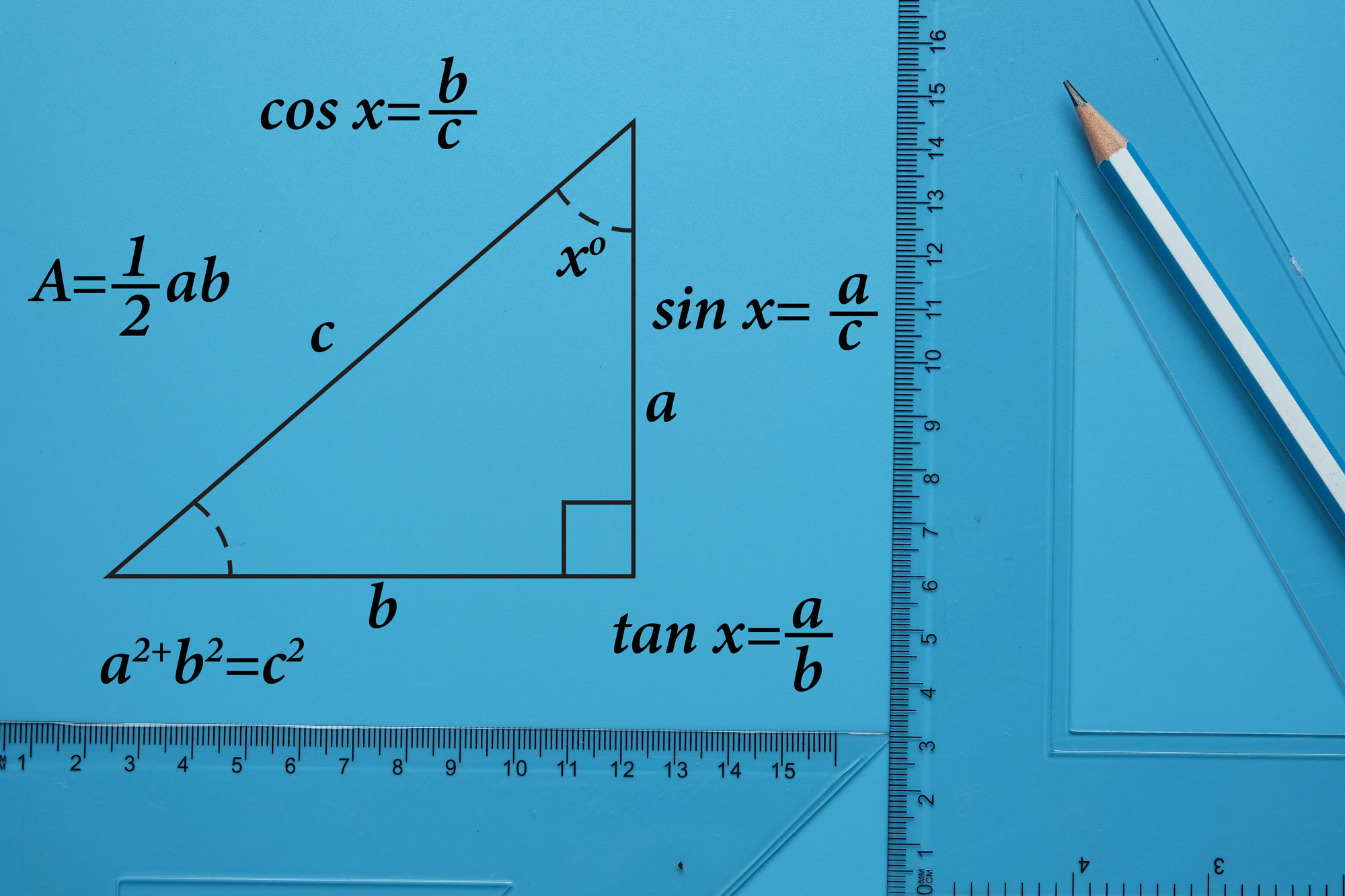
- Isosceles Right Triangle Hypotenuse Calculator

- What is a Right-angled Triangle? - Answered - Right Triangle Activities
- How many lines of symmetry are there in a right angle triangle? - Quora
- VASLANDA Women's High Waist Honeycomb Textured Yoga Pants Tummy Control Ruched Butt Lifting Stretchy Workout Push Up Leggings Booty Scrunch Tights

- Wella Wellaflex Extra Starker Halt Haarspray, Halt: 5/5, 250 ml

- Spotify eGift Card

- SPEEDO Romper BodySuit Activewear Authentic Fitness Cotton Size XL

- Cafe du Nord — Swedish American Hall
